

Result from joint or structural damage due to aberrant or increased biomechanical forces Proprioception, and alteration in abdominal and extensor muscle activation. That include gait and postural dysfunction, increased thoracolumbar stiffness, decreased Persons with LBP exhibit abnormal movement patterns Obesity contributes to factors that promote the development Obesity and LBP occur in tandem as the pain becomes chronic.
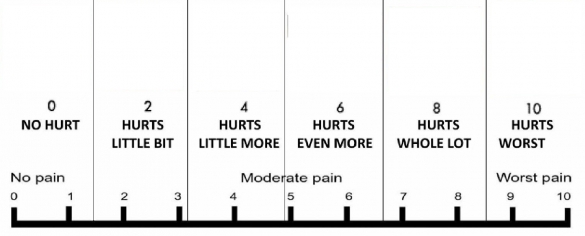
Obesity is more likely to follow the development of LBP. There is no relationship between obesity and LBP. Which of the following statements concerning the relationship between obesity and LBP is TRUE? Primary contribution from psychosocial factors. With chronic LBP, mechanical and biophysiologic factors play a minimal secondary role to the Or repetitive exposures to mechanical stress and age-related degenerative spinal changes. The greatest contributors to LBP episodes are single-event Status, physical activity (e.g., bending, lifting, twisting), repetitive tasks, jobĭissatisfaction, and depression. Modifiable, including higher body mass index (BMI), smoking, lower perceived general health Risk factors for developing LBP can be generally categorizedĪs nonmodifiable, such as old age, female sex, poverty, and lower education level, and What percentage of annual healthcare provider visits in the United States are related to LBP? Occurs among White men (29.2%) compared with Hispanic men (25.7%) and African American menĢ.
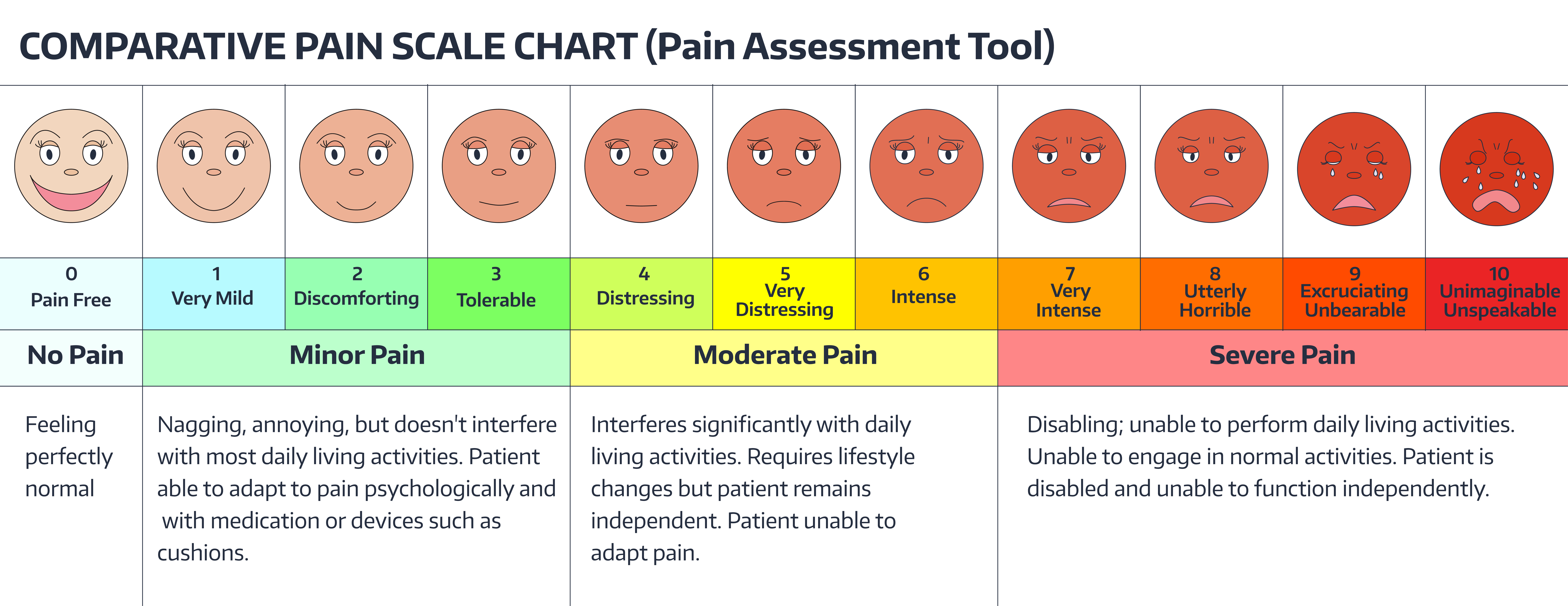
White women are more likely to report LBP (32.2%) compared with AfricanĪmerican women (31.2%) and Hispanic women (28.5%). Least in part) to the type of work typical of the group. Status (35.6% in poor, 27.3% in non-poor) also appear to be factors, likely related (at This is followed by adults 18 to 44 years of age, of whomĢ4.4% reported LBP. Past-three-month LBP (37.3%) compared with 36.5% of adults 65 to 74 years of age and 33.0%
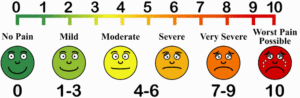
Persons older than 75 years of age were more likely to report Those with a Bachelor's degree or higher (25.5%). Lower educational attainment (33.9%), defined as non-high school graduates, compared with The prevalence was slightly greater for women (30.7%) than men (27.4%) and among those with In 2018, 29% of adults reported LBP in the past three months.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
